Statistical Arbitrage with Options and Derivatives
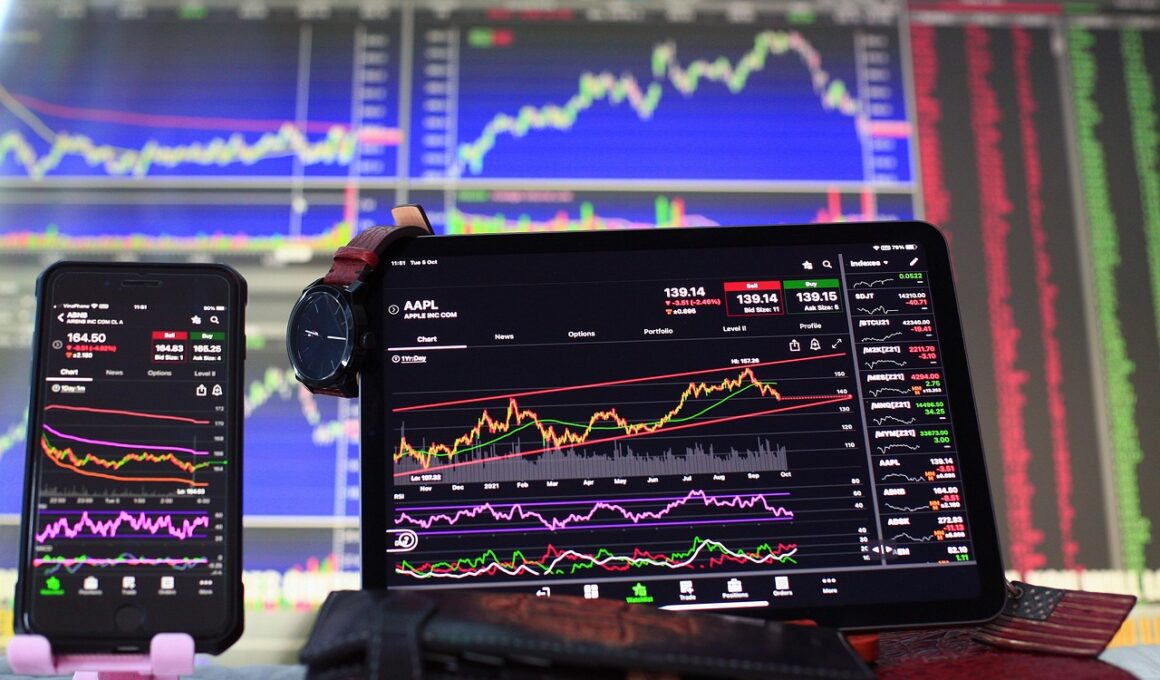
Statistical arbitrage (StatArb) forms a critical part of quantitative finance, especially in the trading of options and derivatives. It involves exploiting pricing inefficiencies to achieve a profit, primarily through mathematical models. Traders often employ complex algorithms to identify trades based on statistical analysis. This could involve examining historical trends and using regression analysis to predict future price movements. A hallmark of StatArb is that it often capitalizes on data discrepancies over time, aiming to exploit market overreactions and underreactions. Moreover, signal generation plays a crucial role, helping traders identify short-term mispricings correlated to market inefficiencies. One significant advantage is that it can be applied to various financial instruments, including stocks, options, and futures. With the aid of high-frequency trading (HFT) systems, the execution speed becomes paramount, facilitating trades that can last from seconds to hours. It’s essential for traders to have a robust risk management framework to mitigate potential losses. Through consistent application, successful statistical arbitrage can yield reliable profits, making it an attractive strategy for active traders and institutional investors alike.
A critical component of statistical arbitrage is understanding how options work within this framework. Options provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price. This flexibility creates various strategies to leverage mispricing opportunities effectively. For instance, traders can employ a long and short option strategy that takes advantage of discrepancies in pricing between the underlying asset and the options. Additionally, derivatives can be priced using models like the Black-Scholes or binomial methods to ascertain their fair value. When mispricings occur between the theoretical price and market price, traders can enter positions that anticipate the corrections. Options and derivatives also allow investors to enhance returns via leverage while managing risk through defined exposure. Consequently, understanding implied volatility becomes essential, as it often differs from the historical volatility of the underlying asset. Building a portfolio that merges statistical arbitrage with options not only diversifies risk but also amplifies potential returns. Thus, this phenomenon is a cornerstone for numerous hedge funds and trading firms aiming for consistent alpha generation in turbulent markets.
Risk Management in Statistical Arbitrage
Effective risk management is indispensable when engaging in statistical arbitrage, particularly with options and derivatives. Traders must measure exposure accurately to unexpected market movements as these instruments inherently carry higher risk. Variables such as delta, gamma, and vega need close monitoring to understand how an option’s price will react to changes in market conditions. By employing sophisticated risk metrics, such as Value at Risk (VaR), traders can quantify potential losses over a set period. Utilizing stop-loss orders effectively further aids in limiting downside exposure, proactively managing adverse market events. Additionally, diversification serves as a hallmark of sound risk management, spreading investments across various instruments or strategies to lower overall risk exposure. Importantly, maintaining a disciplined approach to trading can help avoid emotional decision-making, often resulting in poor outcomes. Another recommended practice includes routinely backtesting strategies against historical data, enabling traders to assess potential performance and refine their models. Adapting to changing market conditions through systematic reviews fosters resilience, allowing traders to pivot strategies effectively. Consequently, proficient risk management can significantly enhance long-term success and sustainability in the statistical arbitrage landscape.
The integration of machine learning techniques and advanced statistical methods into statistical arbitrage has transformed the landscape of options and derivatives trading. By employing algorithms that can analyze vast datasets in real time, traders can uncover hidden patterns and statistical relationships that human analysis may overlook. For instance, logistic regression and decision trees can be utilized to predict pricing movements based on a multitude of variables. Moreover, machine learning algorithms can adapt dynamically, learning from new data inputs and ensuring that they remain relevant in fluctuating market conditions. This allows for continual refinement of trading strategies, leading to improved performance over time. The implementation of these advanced techniques also enhances the ability to conduct sensitivity analysis, predicting how changes in market parameters will affect potential outcomes. However, an essential aspect of leveraging machine learning lies in the interpretability of algorithms, ensuring transparency and understanding of trading decisions. Therefore, while embracing technology is vital for staying competitive, maintaining a balance between automated decision-making and human oversight remains paramount for navigating financial markets efficiently.
Developing a Statistical Arbitrage Strategy
To develop a robust statistical arbitrage strategy using options and derivatives, practitioners must follow systematic steps. Initial research often involves identifying suitable market inefficiencies, which generally stem from price inaccuracies caused by behavioral biases or market mechanics. Empirical analysis then derives signals to detect these mispricings by utilizing quantitative techniques such as autocorrelation tests and cointegration analysis. Next, traders create a model to predict price movements based on historical data correlation, aiming for high statistical significance. Once potential trades are identified, risk analysis becomes paramount, allowing traders to evaluate position sizing and exposure effectively. Following these phases, traders backtest their strategies against historical data, validating the reliability of the model across different market conditions. This iterative process helps refine the strategy, adjusting parameters until desired performance metrics are achieved. Post-backtesting, real-world application requires continuous monitoring to ensure that models adapt to ongoing market changes. This comprehensive approach to developing a statistical arbitrage strategy facilitates a well-structured, disciplined pathway to potentially achieving consistent profits in the volatile trading environment.
Furthermore, establishing a performance measurement framework plays a vital role in assessing the effectiveness of statistical arbitrage strategies. Common metrics for evaluation include the Sharpe ratio, which measures return per unit of risk, and the Sortino ratio, which focuses exclusively on downside risk. Incorporating these metrics provides insight into both absolute and risk-adjusted returns over time. Trade execution efficiency also reflects on performance; minimizing transaction costs ensures that strategies do not erode potential profits. Leveraging platforms that support algorithmic trading and enable low-latency order execution can enhance profitability through timely market positions. Regular performance review intervals allow for benchmarking strategies against predefined expectations and refining them when necessary. Peer comparisons can also yield insights, ensuring that traders remain competitive within their performance cohort. Additionally, rate of return assessments on different time frames can provide clarity on strategy effectiveness over short and long-term periods. Continuous improvement based on performance metrics not only bolsters confidence but also instills a culture of accountability within trading operations.
The Future of Statistical Arbitrage
As technology evolves, the future of statistical arbitrage, particularly with options and derivatives, is likely to witness significant transformations. Innovations such as blockchain technology and cryptocurrency derivatives are shaping new opportunities in analyzing volatility and price discrepancies. As markets become increasingly interconnected, the availability of real-time data is expected to aid traders in refining their models and deriving actionable signals more effectively. Additionally, advancements in artificial intelligence, particularly in natural language processing, will enable traders to incorporate sentiment analysis into their strategies, offering insights from news and social media sources. Moreover, regulatory changes will necessitate adaptations, compelling traders to ensure compliance within rapidly evolving financial landscapes. This adaptation will likely call for enhanced collaboration among professionals across disciplines to integrate insights from engineering, finance, and mathematics. As firms refine their use of machine learning, the demand for professionals skilled in both finance and technology will rise accordingly. The future landscape of statistical arbitrage stands poised for continued disruption, requiring traders to embrace change and innovate to thrive in a competitive environment.
In conclusion, statistical arbitrage represents a remarkable convergence of quantitative analysis and trading philosophy, especially within the realm of options and derivatives. The combination of mathematical models, risk management, and continuous performance evaluation serves as the nucleus for effective trading strategies. By embracing technology, traders can open new avenues for profit, armed with the ability to process vast datasets swiftly. Central to success will be the integration of systematic frameworks with adaptive models that respond to market conditions. Traders must balance sound strategies with robust risk management to navigate the inherently volatile financial landscape. Moreover, clear evaluation metrics will provide insights necessary for continuous improvement. As the field evolves, staying abreast of technological advancements will become essential for maintaining competitive benefits. The prospects for statistical arbitrage remain bright, promising ongoing opportunities for those willing to innovate and adapt. In summary, the marriage of statistical techniques with modern trading paradigms is not only a powerful tool but a pathway toward sustained success in the dynamic trading universe.