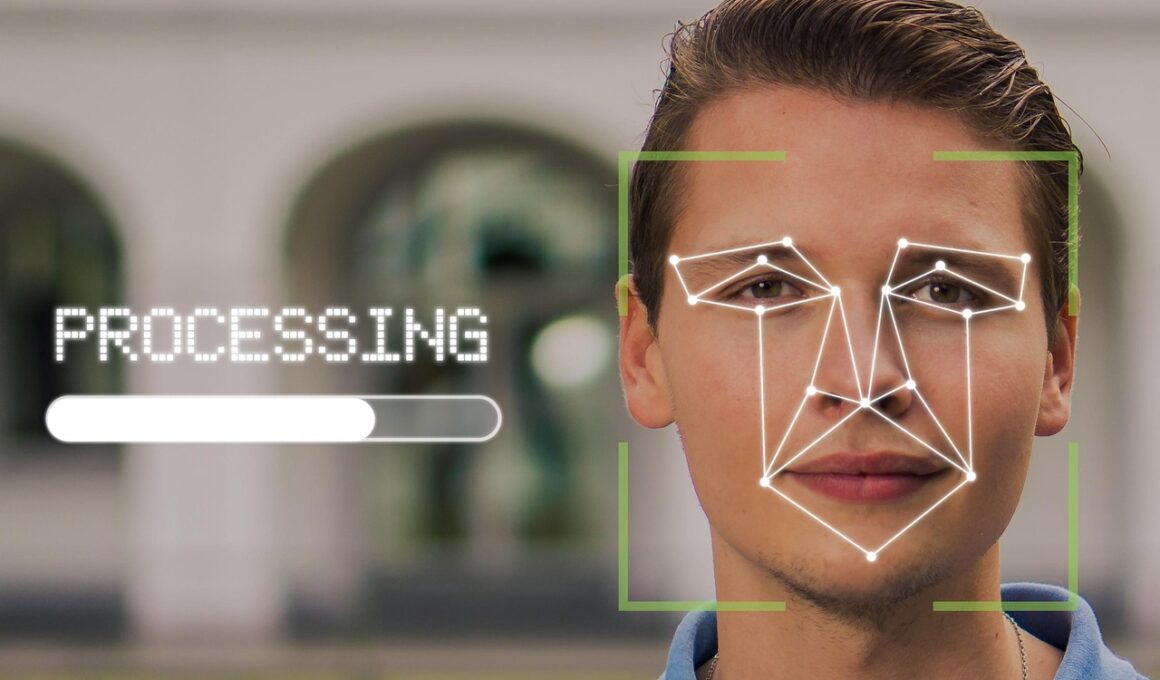
Enhancing Microfinance Security with Biometric Authentication
In today’s digital age, microfinance institutions face unprecedented security challenges. Traditional security measures often fall short when protecting sensitive financial data from emerging threats. With the rise of financial technology (FinTech), innovative solutions are now available to enhance security. Biometric authentication is one such solution, utilizing unique human characteristics to verify identity effectively. This method minimizes risks associated with traditional passwords that users often forget or expose to phishing attacks. By implementing biometric systems, microfinance institutions can prevent unauthorized access and reduce fraud, thereby fostering a safer transaction environment. Additionally, biometric authentication provides convenience to clients, ensuring quick access to their accounts without the hassles of forgotten passwords or lengthy recovery processes. Overall, the integration of biometric verification not only safeguards sensitive data but also improves user experiences, ultimately contributing to stronger customer trust and loyalty. As technology continues to evolve, embracing these advancements is essential for securing financial services in microfinance frameworks across the globe. Institutions must be proactive in adopting these technologies to stay ahead in terms of competitiveness and security.
Integrating biometric authentication into microfinance platforms can significantly enhance security protocols. Microfinance stakeholders must evaluate several biometric modalities including fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, and iris recognition. These methods have varying levels of accuracy and user acceptance. For instance, fingerprint scanning is widely accepted due to its simplicity and ease of use. In contrast, facial recognition technology offers a non-intrusive approach without requiring physical contact. Research indicates that users may prefer biometric methods over traditional authentication as they simplify the user experience. However, it is essential to address privacy concerns related to biometric data collection. Proper guidelines must be in place to ensure compliance with data protection regulations and ethical standards. Potential limitations also exist, especially in regions with limited technology infrastructure. The success of biometric authentication in microfinance applications largely depends on educating clients about its benefits and reassuring them about data security. Institutions should provide transparent information on how biometric data will be used, stored, and protected. Overall, with the right infrastructure and stakeholder engagement, implementing biometric authentication can revolutionize security in the microfinance sector.
Benefits of Biometric Authentication in Microfinance
Biometric authentication introduces several advantages for microfinance institutions aiming for fortified security measures. Primarily, the demographic typically served by microfinance includes individuals lacking access to conventional banking services. By utilizing unique physical traits for verification, these institutions can open up banking services to underserved populations, enabling a broader customer base. Furthermore, the implementation of biometric systems fosters a sense of security and reduces instances of identity theft. Microfinance customers often face financial vulnerabilities, making effective security essential for their empowerment. Moreover, the user experience is significantly enhanced through swift log-in processes without the need for memorizing complex passwords. The focus on customer convenience ensures that clients have seamless access to their accounts. Additionally, biometric systems can provide tailored financial options to clients, as their unique data can help institutions analyze their behaviors and preferences. This data-driven approach leads to more personalized services, thereby improving customer satisfaction and retention rates. In essence, instituting biometric authentication can resolve numerous security challenges while promoting inclusivity and client satisfaction in microfinance.
Despite the advantages of biometric authentication, microfinance institutions must remain vigilant concerning potential challenges. One of the primary concerns revolves around the technology’s reliability and accuracy, as biometric systems can produce false positives or negatives. Such discrepancies can undermine user trust if clients are frequently misidentified during authentication. Therefore, institutions should invest in high-quality biometric solutions to ensure precision and effectiveness. Additionally, the initial implementation costs can pose a hurdle for smaller organizations within the microfinance sector. These entities might struggle to allocate sufficient resources for upgrading their existing systems. To address this concern, financial institutions can consider partnerships or collaborations with FinTech companies specializing in biometric technologies. These collaborations may provide cost-effective options while offering access to robust security tools. Furthermore, the legal and ethical ramifications of managing biometric data cannot be overlooked. Ensuring compliance with local laws governing data protection and privacy is crucial. Institutions must prioritize transparency in their operations to maintain customer trust. By effectively navigating these challenges, microfinance institutions can leverage biometric authentication to enhance their security landscape.
Future Trends in Biometric Technology
The future of biometric technology in microfinance holds remarkable potential as advancements continue to evolve. Emerging innovations such as behavioral biometrics analyze clients’ patterns and interactions to enhance security further. This approach complements existing biometric methods, making unauthorized access even more complicated. By analyzing the way users engage with their devices—a specific typing rhythm, for instance—institutions can implement additional layers of security. Moreover, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in biometric authentication can facilitate real-time monitoring, identifying potential threats much quicker. As AI technology advances, its collaboration with biometrics will help refine accuracy and user experiences. Institutions must stay abreast of these advancements to remain competitive in the industry. The incorporation of blockchain technology may also improve data security with decentralized storage systems that safeguard biometric information. Such innovations will give customers greater confidence in the security of their identities. However, institutions should also remain cognizant of ethical considerations surrounding biometric data usage. Addressing customer concerns transparently will be vital as these technologies develop. Overall, the future promises tremendous possibilities for enhancing microfinance security through biometric solutions.
Educational outreach plays a vital role in successfully implementing biometric authentication in microfinance. Institutions must actively engage with their clients to ensure comprehensive understanding of the benefits and applications of biometric systems. Development of workshops, informational sessions, and promotional materials can facilitate this process. Importantly, organizations should highlight how these technologies address security concerns and enhance user experiences. A significant aspect of this education should include addressing misconceptions about biometric data collection. By informing clients about data protections, including encryption and secure storage, organizations can alleviate potential fears surrounding privacy. Furthermore, obtaining feedback from clients about their experiences with biometric authentication can provide valuable insights for future enhancements. Engaging clients in the implementation process fosters trust and loyalty, essential components in services associated with finance. Collaborations with local communities may also bolster acceptance and encourage adoption of biometric technologies. Additionally, the ongoing evaluation of these authentication systems will help ensure their effectiveness and reliability. By prioritizing education, microfinance institutions can address potential challenges and maximize the benefits of biometric authentication for their clients.
Conclusion
In conclusion, biometric authentication represents a transformative opportunity for microfinance security enhancement. As challenges in the digital landscape grow, embracing these sophisticated technologies is essential for microfinance institutions to protect sensitive customer information while ensuring convenience. By adopting biometric solutions, organizations can foster a safer transaction environment, enhance customer trust, and improve overall service delivery. It is paramount for institutions to remain proactive in addressing potential risks associated with biometric systems while promoting transparency and user education. Collaboration with technology partners can facilitate effective implementations and innovations that address existing challenges within microfinance. By investing in biometric authentication, microfinance institutions position themselves strategically amid rapid technological evolutions while remaining competitive. Additionally, the potential for inclusivity through these technologies can empower underserved communities, enabling access to financial services. This not only benefits the institutions but also contributes positively to the broader financial ecosystem. Therefore, the path toward enhanced security with biometric authentication stands essential in the future landscape of microfinance, driving innovation, trust, and growth in an increasingly digital world.